No fear: it´s just Skin ultrasound Doppler!
Although scanning in B-mode provides useful information about skin lesions, Doppler
ultrasound allows us to study phenomena such as inflammation and neovascularization
which are of interest for the biology and diseases of the skin.
Physicians fear Doppler:
1) Because it is very mathematics-physics related matter (formulae fear!)
2) Because the example of ambulance siren pitch does not help much (and makes your mind go with the ambulance!)
Let´s imagine….
Doppler frequency concept
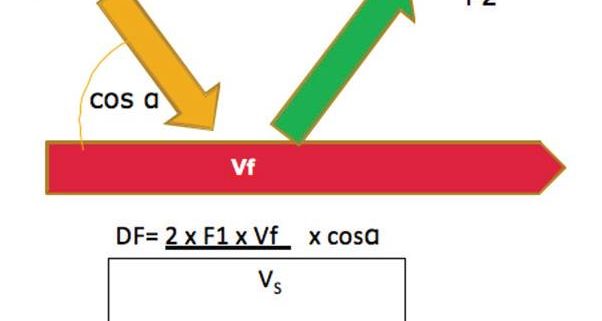
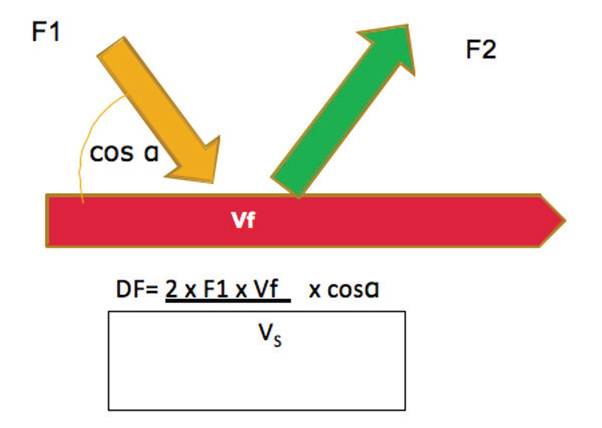
Imagine that with your equipment you produce a sound wave with a
given frequency (F1) that will hit the blood running in a blood vessel of
the dermis .
The wave reflected by the blood moving at a given velocity (Vf) will
have a different frequency (F2) from the one that was emitted.
This change in frequency (DF) is what is called the Doppler frequency.
Mathematically, Christian Doppler connected all these variables in
an equation, such that by calculating the frequency change you could
determine the velocity the blood flowing in the blood vessel.
Two factors should also be taken into account: the speed of the wave
through the skin (Vs) (1540 cm/sec) and the cosine of the angle made
between the wave and the blood vessel (cosα).
The angle of insonation is an important factor which can influence
the determination of fluid velocity.
Insonation angles ranging from 30ºor 60º are considered to produce
acceptable measurement error.
Fortunately, all these parameters and calculations are performed
directly by the computer giving us immediately all the information
regarding the movement of the blood in any blood vessel.
Doppler modes in cutaneous ultrasound
The information on the flows and velocities of the blood calculated by
the processing unit are represented by colors or curves known as modes.
There are three modes useful in cutaneous ultrasound:
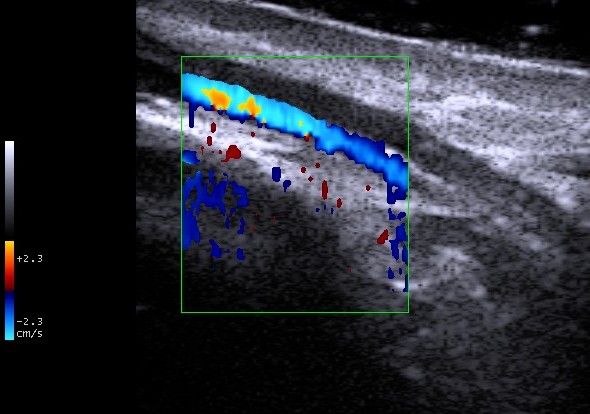
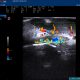
1) Color Doppler: The speed and the directions of the fluid are coded
in colors (usually blue and red) and in color intensity, respectively, giving
us a picture of the average speed in a bidimensional image .
Color Doppler retropalpebral vein
2) Power Doppler or Intensity Doppler: This is based on the intensity
change of the doppler frequency and it is not so influenced by the angle
of insonation.
It is represented by a single color (usually yellowish-orange) and
includes a visual scale of this color’s tones . It does not provide
information on the direction of the fluid and is primarily used to detect
very slow fluxes.
Nowadays it is not so much used as the result of the development of
improved Color Doppler systems that are able to detect slow flows as
well as the Power Doppler.
Power doppler pyogenic granuloma
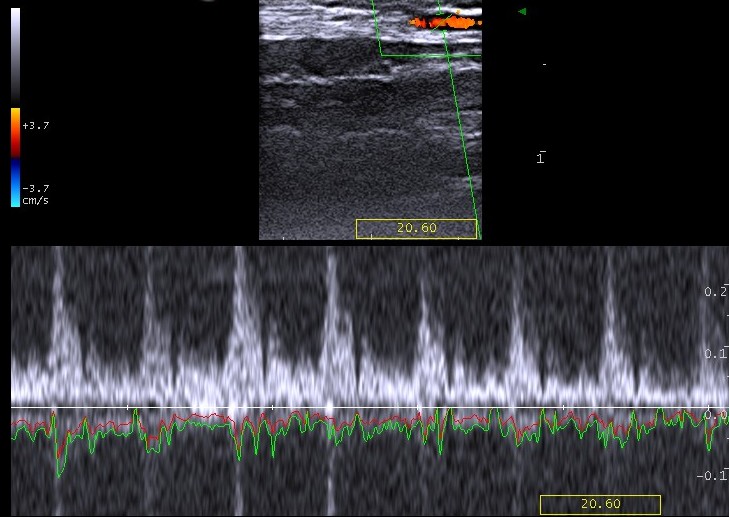
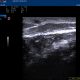
3) Pulsed Doppler: It represents fluid velocities in the form of a curve.
In this way we can measure the maximum and minimum velocity of
blood flow.
Temporal artery flow
Learning doppler is an endless task: everytime I revisit my Doppler principles I find new explanations to skin vascularization phenomena.



Dejar un comentario
¿Quieres unirte a la conversación?Siéntete libre de contribuir