Congenital focal fat atrophy in an infant: value of skin ultrasound
Skin ultrasound gets deeper in evaluating subcutaneous cellular tissue alterations.
Subcutaneous fatty tissue may proliferate in the case of localized focal increase in an orderly or in a dystrophic arrangement such as cellulite.
In some occasions there is generalized lypoatrophies such as in Sipple syndrome and in some occasions loss is focal such as in steroid injection or lupus panniculitis.
CASE
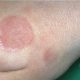
- 7 -year- old boy
- Congenital atrophic plaque in dorsal arm since new-born. No obstetric trauma reported by father
- Stability in shape and depth.
Skin ultrasound is performed to assess this lesion and make differential diagnosis with lesions such as focal aplasia cutis or deep morphea.
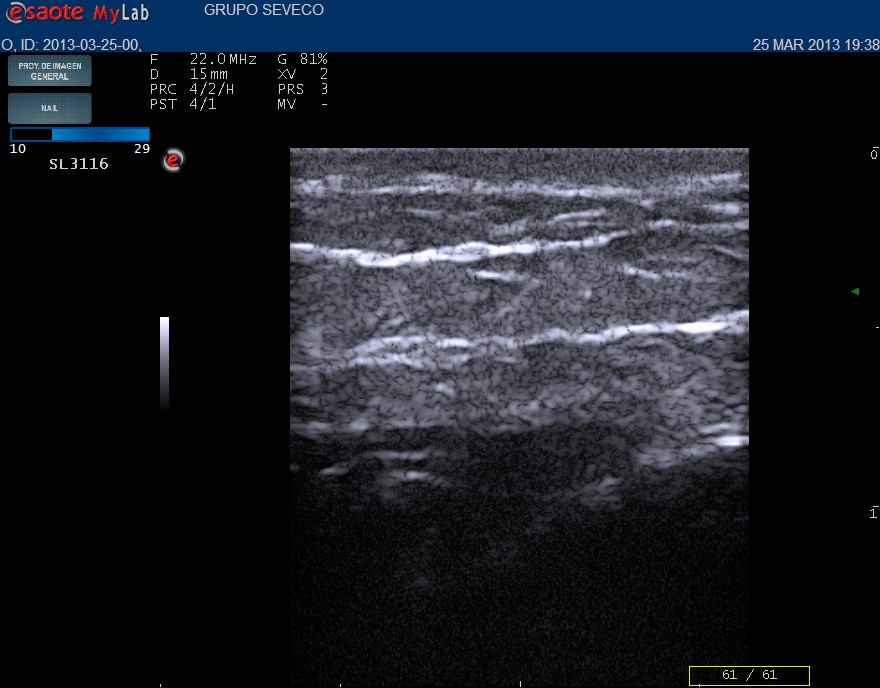
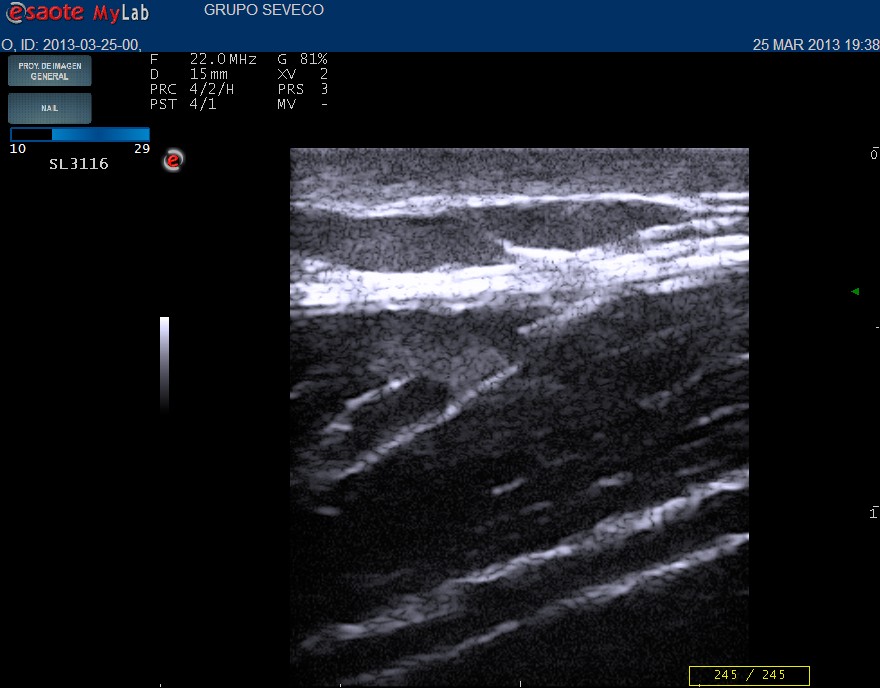
Norma perilesional area Atrophic area
Ultrasound report
Dermal thickening in comparison with asymptomatic area
Absence of inflammatory signs in dermis
Subcutaneous fatty tissue reduction of both u lower compartments with thickening of deep fascia . Decrease in septa density respect to surrounding normal tissue.
Absence of doppler flow in subcutaneous tissue.
DIAGNOSIS
Congenital focal fat atrophy
TAKE HOME MESSAGES
- Subcutaneous tissue alterations can be studied with skin ultrasound.
- Analysis of normal or abnormal sonographic structure is essential.
- Sign of inflammation van be assessed and offered to take a further invasive diagnosis and treatment.
It´s again clear that an effort in standarization in skin US nomenclature must be reached to communicate, understand and share our findings and share number of cases power.













Dejar un comentario
¿Quieres unirte a la conversación?Siéntete libre de contribuir